Backscatter spam is relatively new problem in spam. Backscatter (also known as outscatter, misdirected bounces, blowback or collateral spam) is incorrectly automated bounce messages sent by mail servers, typically as a side effect of incoming spam.
❗ Problem Description
Usually when email is sent by spammers to mail server they use auto-generated email addresses for both senders and receivers. This ends up being something similar to [email protected] sending email to [email protected]. While it's very unlikely blablabla@ will ever get such email, servers around the world are setup to inform the sender that he most likely mistyped e-mail address or simply recipient is no longer working for the company. While it's a good thing to do that so that your customer can be aware of e-mail not being delivered, it also creates a lot of useless mail flow when spammers sent hundreds of emails to non-existing addresses at your e-mail server and you want to try to notify them all. Since sender is usually spoofed it creates lots of mail traffic that shouldn't be generated in the first place. If you don't block your server from sending out such responses you're often end up on Backscatter anti-spam lists.
What makes it worst is that if you get your e-mail server on such spam list you either have to pay money to remove it from the list or wait 4 weeks for it to be auto removed. While I've not seen many servers using this spam list it's entirely possible there are servers out there that throw out your emails just because you're on that list.
To make sure that your server doesn't end up on that list there are few ways to protect your Microsoft Exchange Server.
🔹 Solution – Protect Microsoft Exchange using GFI Mail Essentials 20
If you have GFI Mail Essentials 20 there are 2 steps to make your server secure against backscattering. You have to enable Directory Harvesting anti-spam filter, and you have to change SMTP Transmission Filtering.
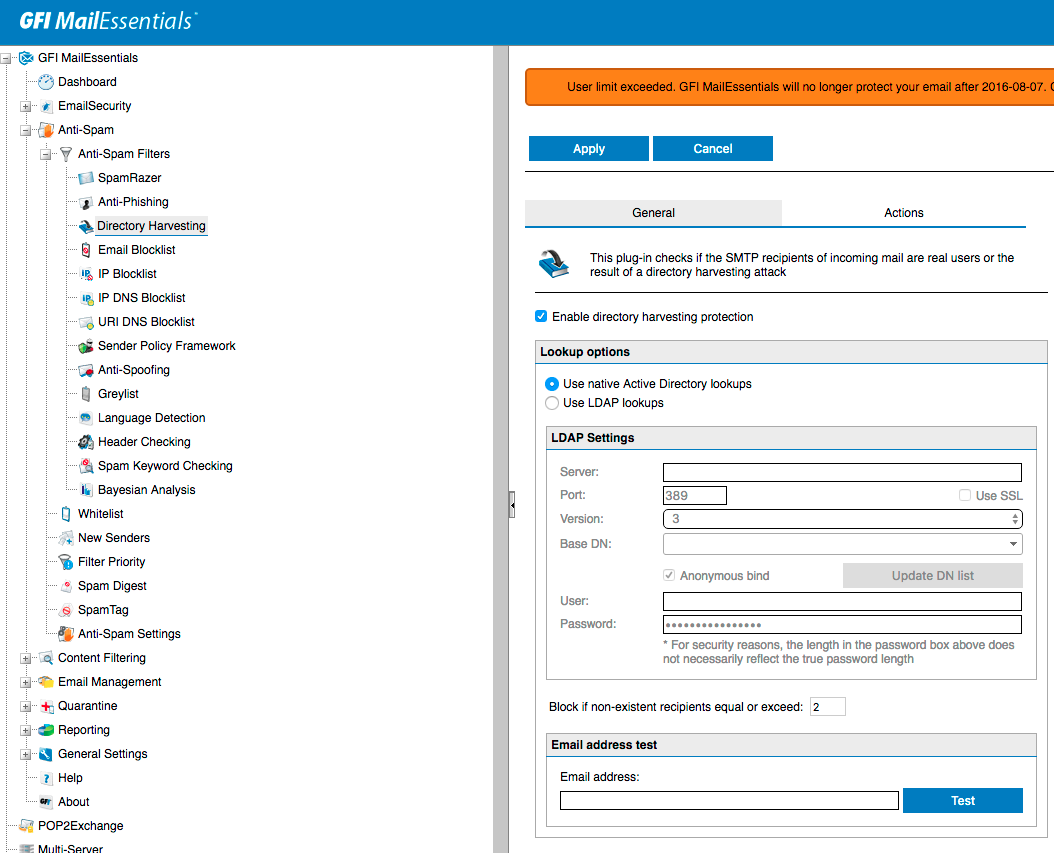
Enabling Directory Harvesting is as simple as going into Anti-spam, Anti-spam Filter and Directory Harvesting option. Since our GFI Mail Essentials is installed on Exchange server directly we can use the option Use native Active Directory lookups. We also recommend setting Block if non-existent recipients equal or exceed to 2 addresses.
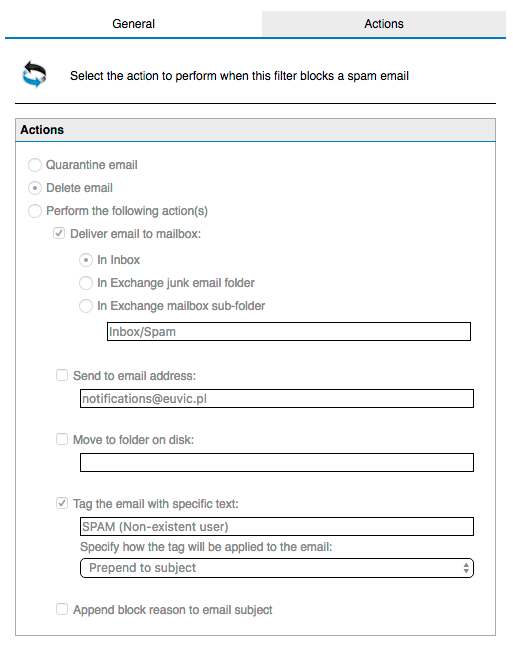
On second tab, if it's not greyed out you should choose Delete email option. There's no real reason to quarantine the email or keep them in different form anyways. In our case as you can see it's greyed out which basically means we already have next step configured which is making sure the verification of e-mails is done on SMTP Transmission level rather then during Full Email Transmission.
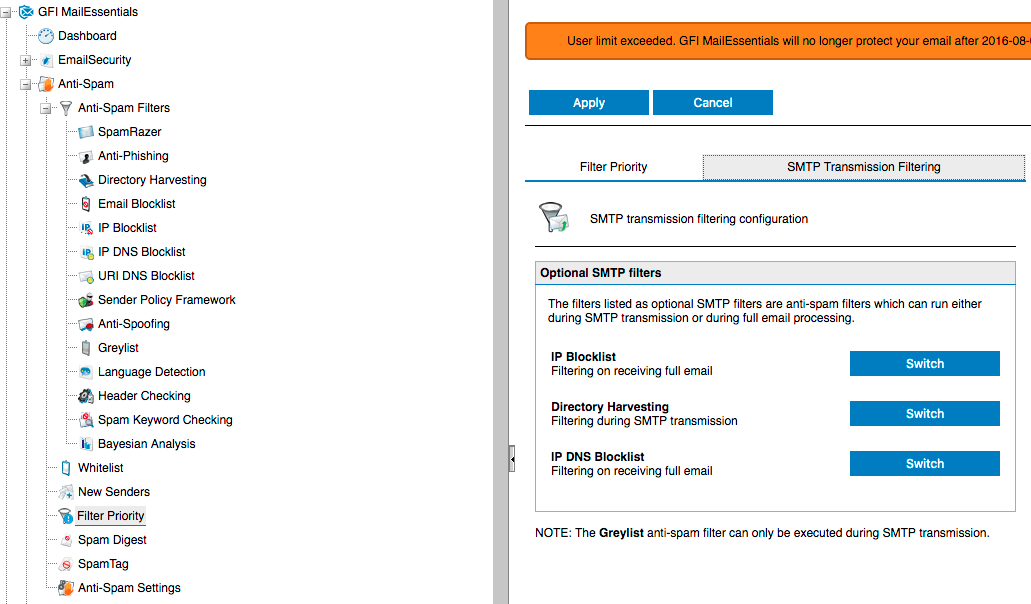
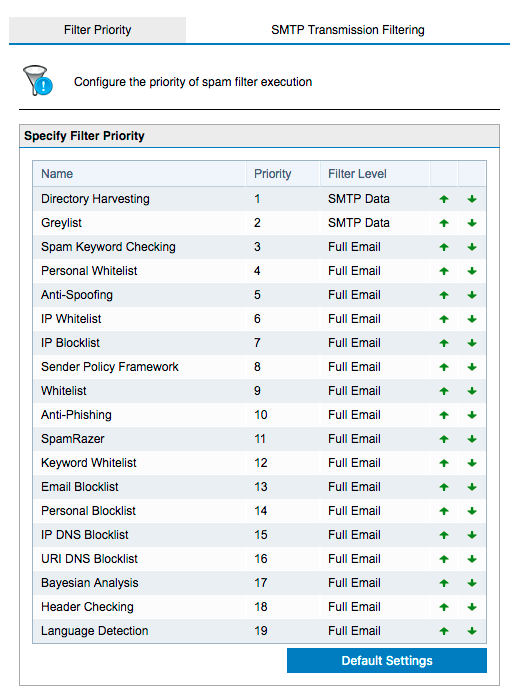
Now go to Anti-spam, Filter Priority and switch tab to SMTP Transmission Filtering. On this tab make sure under Directory Harvesting option it says Filtering during SMTP transmission. If it says something different make sure to press Switch and then Apply. This step is very important. Otherwise even thou Directory Harvesting will work just fine but it will still send emails back to fake senders and cause backscatter.
After this change Directory Harvesting on Filter priority should be on top of the list, and the Filter Level should be SMTP Data.
This way Microsoft Exchange server sends only NDR (Non Delivery Reports) to real senders making sure your server doesn't spam other servers by accident.
🔹 Solution – Protect Microsoft Exchange by disabling NDR for all domains
If you don't have GFI MailEssentials installed you can also go and disable NDR's. While NDR's are useful they can cause problems as described above. Spammers use it to find valid addresses to send more directed spam rather then auto-generated email addresses. In Microsoft Exchange 2013 or Microsoft Exchange 2016 you can disable Non Delivery Reports (NDR) with a simple PowerShell command.
Microsoft Exchange 2013/2016 PowerShell to control NDR:
# In this example we disable Non Delivery reports to “baddomain.com”. Set-RemoteDomain baddomain.com -NDREnabled $false # If we later wanted to re-enable the NDR`s to this domain it would be. Set-RemoteDomain baddomain.com -NDREnabled $true # If we want to disable all NDR's Set-RemoteDomain Default -NDREnabled $false # And just allow it for some... Set-RemoteDomain trusteddomain.com -NDREnabled $true
While disabling NDR's help to solve Backscattering it should be done carefully to not cripple your email system in the process.
🔹 Solution – Protect Microsoft Exchange using builtin Antispam
Another option to protect Microsoft Exchange server from backscatter spam is to create recipient filtering that's available in builtin anti-spam agents.
For Exchange 2003 this is described in step 2 in this Microsoft KB article
For Exchange 2007 Hub servers and later you first need to enable the anti-spam functionality. It's described on Microsoft Technet. After it's enabled go to Edge Transport (or Hub Transport as appropriate) > Anti-spam tab > Recipient Filtering and enable it as described here.
For Exchange 2010, instructions are similar to Microsoft Exchange 2007. Go to Properties > Blocked recipients and ensure Block messages set to recipients that do not exist in the directory is ticked as described on Microsoft Technet.
For Exchange 2013, see here to enable Exchange anti-spam and then here and here to stop backscatter. The EMC commands are:
Set-RecipientFilterConfig -Enabled $true Set-RecipientFilterConfig -RecipientValidationEnabled:$true
🔹 Notes – PowerShell commands
Microsoft Exchange allows disabling Delivery Reports which is often used by people to track of their email has been read. While this option doesn't cause backscatter many companies don't wish to send our Delivery Reports so that their users can notify senders if email has arrived on their own agenda. We can do that per domain basis (banning sending Delivery Reports to just one or few customers) or by using global option.
To do that you can simply use below powershell commands to
# Disable delivery reports to yourcompetitor.com domain Set-RemoteDomain yourcompetitor.com -DeliveryReportEnabled $false # Enable delivery reports to yourcompetitor.com domain Set-RemoteDomain yourcompetitor.com -DeliveryReportEnabled $false # Disable delivery reports to all domains Set-RemoteDomain Default -DeliveryReportEnabled $false # Enable delivery reports to all domains Set-RemoteDomain Default -DeliveryReportEnabled $true
Keep in mind it's entirely possible to block NDR or Delivery Reports to all senders and just allow those for few important customers. The proper way to do this would be:
Set-RemoteDomain Default -DeliveryReportEnabled $false -NDREnabled $false Set-RemoteDomain yourbestcustomer.com -DeliveryReportEnabled $true -NDREnabled $true Set-RemoteDomain yourothercustomer.com -DeliveryReportEnabled $true -NDREnabled $true Set-RemoteDomain mycustomer.com -DeliveryReportEnabled $true -NDREnabled $true
If you wish to verify your NDR, DeliveryReports settings you can check them globally by using following PowerShell query
Get-RemoteDomain | ft -AutoSize Name, DomainName, AllowedOOFType, NDREnabled, DeliveryReportEnabled, MeetingForwardNotificationEnabled,AutoReplyEnabled, AutoForwardEnabled, NDRDiagnosticInfoEnabled
🔹 Notes – NDR Codes Description
Please be aware that NDR's are essential debugging tools. Using NDR's can often give you clues about problems in your system. Below you can find some useful NDR codes.
| Common NDR Codes, Possible Cause, and Troubleshooting Information | |
| Code | Possible Cause – Troubleshooting |
|
4.3.1 |
Out-of-memory or out-of-disk space condition on the Exchange server. Potentially also means out-of-file handles on IIS. |
|
4.3.2 |
Message deleted from a queue by the administrator via the Queue Viewer interface in Exchange System Manager. |
|
4.4.1 |
Host not responding. Check network connectivity. If problem persists, an NDR will be issued. |
|
4.4.2 |
Connection dropped. Possible temporary network problems. |
|
4.4.6 |
Maximum hop count for a message has been exceeded. Check the message address, DNS address, and SMTP virtual servers to make sure that nothing is causing the message to loop. |
|
4.4.7 |
Message expired. Message wait time in queue exceeds limit, potentially due to remote server being unavailable. |
|
5.0.0 |
Generic message for no route is available to deliver a message or failure. If it is an outbound SMTP message, make sure that an address space is available and have proper routing groups listed. |
|
5.1.0 |
Message categorizer failures. Check the destination addresses and resend the message. Forcing rebuild of Recipient Update Service (RUS) may resolve the issue. |
|
5.1.1 |
Recipient could not be resolved. Check the destination addresses and resend the message. Potentially e-mail account no longer exists on the destination server. |
|
5.1.3 |
Bad address. |
|
5.1.4 |
Duplicate SMTP address. Use LDIFDE or script to locate duplicate and update as appropriate. |
|
5.2.1 |
Local mail system rejected message, “over size” message. Check the recipient’s limits. |
|
5.2.3 |
Message too large. Potentially the recipient mailbox is disabled due to exceeding mailbox limit. |
|
5.3.3 |
The remote server has run out of disk space to queue messages, possible SMTP protocol error. |
|
5.3.5 |
Message loopback detected. |
|
5.4.0 |
Authoritative host not found. Check message and DNS to ensure proper entry. Potential error in smarthost entry or SMTP name lookup failure. |
|
5.4.4 |
No route found to next hop. Make sure connectors are configured correctly and address spaces exist for the message type |
|
5.4.6 |
Categorizer problems with recipient. Recipient may have alternate recipient specified looping back to self. |
|
5.4.8 |
Looping condition detected. Server trying to forward the message to itself. Check smarthost configuration, FQDN name, DNS host and MX records, and recipient policies. |
|
5.5.0 |
Generic SMTP protocol error. |
|
5.5.2 |
SMTP protocol error for receiving out of sequence SMTP protocol command verbs. Possible to low disk space/memory of remote server. |
|
5.5.3 |
Too many recipients in the message. Reduce number of recipients in message and resend. |
|
5.7.1 |
Access denied. Sender may not have permission to send message to the recipient. Possible unauthorized SMTP relay attempt from SMTP client. |